Price floor is a price control typically set by the government that limits the minimum price a company is allows to charge for a product or service its aim is to increase companies interest in manufacturing the product and increase the overall supply in the market place.
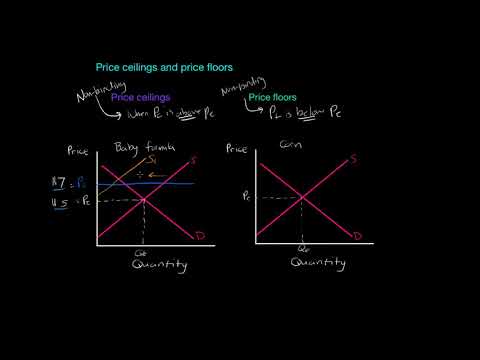
Define price ceilings and price floors give examples of both.
What is the purpose of setting a price floor and price ceiling.
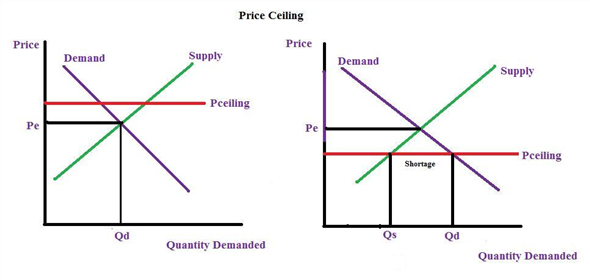
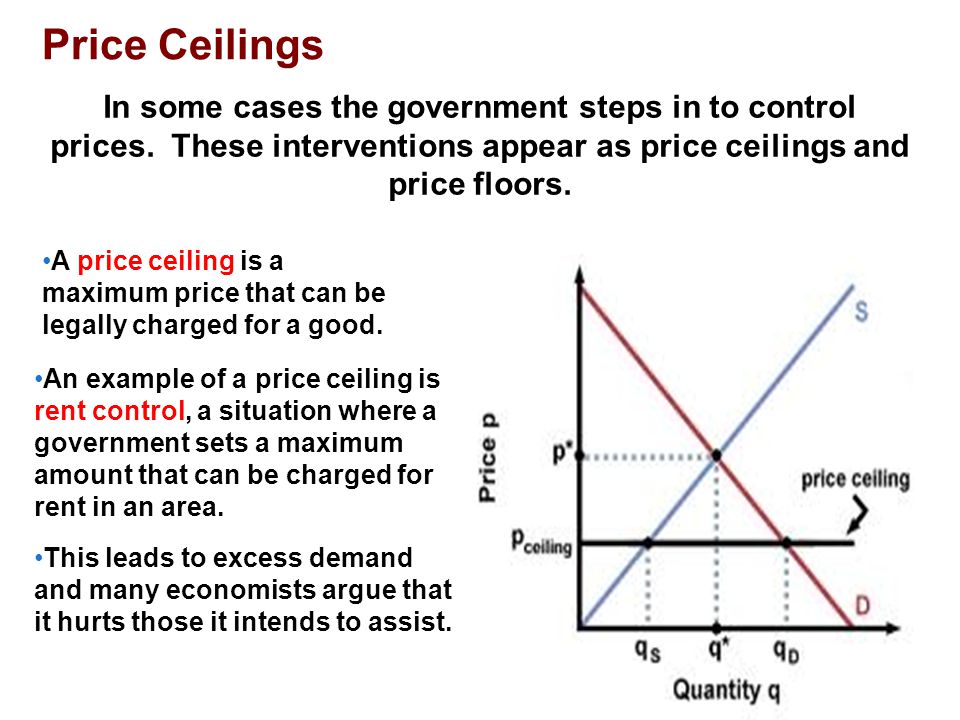
A price ceiling is the legal maximum price for a good or service while a price floor is the legal minimum price.
Government imposed price ceilings on gasoline after some sharp rises in oil prices.
Define price ceiling and price floor and give an example of each.
We assume that the equilibrium price is 25 per unit for a certain good.
But this is a control or limit on how low a price can be charged for any commodity.
It is legal minimum price set by the government on particular goods and services in order to prevent producers from being paid very less price.
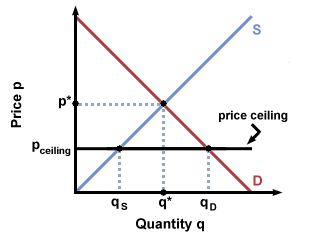
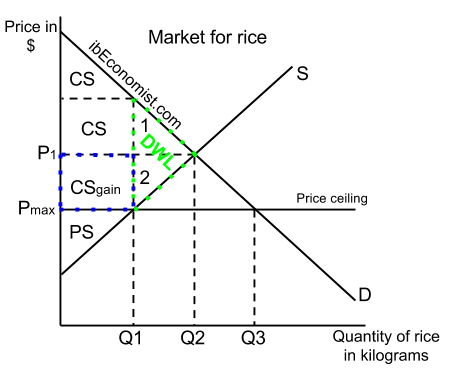
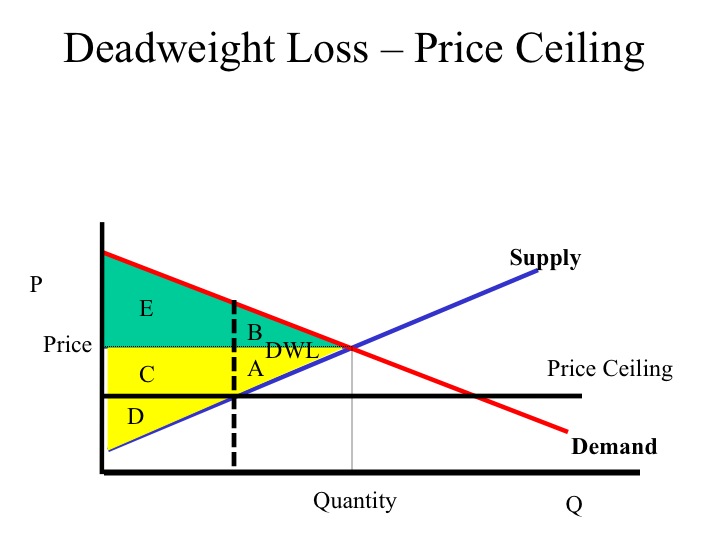
If the government sets a price ceiling of 15 per unit for this good the quantity demanded will be 3 500 units whereas the quantity supply will be 1 500 units.
Like price ceiling price floor is also a measure of price control imposed by the government.
The original intersection of demand and supply occurs at e 0 if demand shifts from d 0 to d 1 the new equilibrium would be at e 1 unless a price ceiling prevents the price from rising.
Basically the purpose of the price ceiling is to make prohibition for the people who charge high prices from their customers and this protect and prevent them.
If the price is not permitted to rise the quantity supplied remains at 15 000.
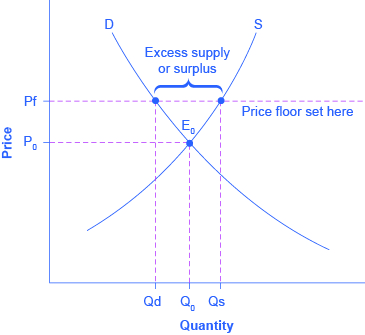
The price floor definition in economics is the minimum price allowed for a particular good or service.
However prolonged application of a price ceiling can lead to black marketing and unrest in the supply side.
National and local governments sometimes implement price controls legal minimum or maximum prices for specific goods or services to attempt managing the economy by direct intervention price controls can be price ceilings or price floors.
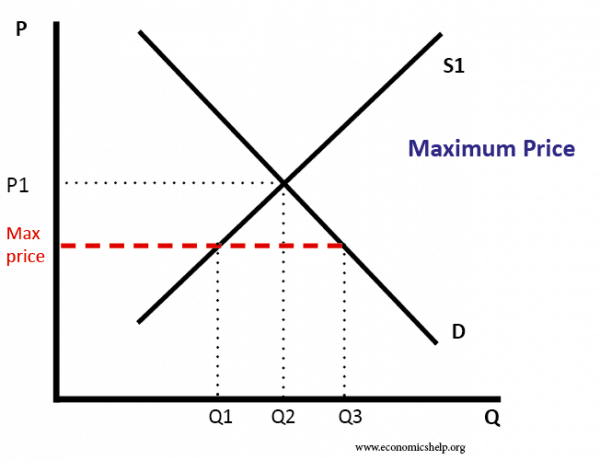
Now the government determines a price ceiling of rs.
Here in the given graph a price of rs.
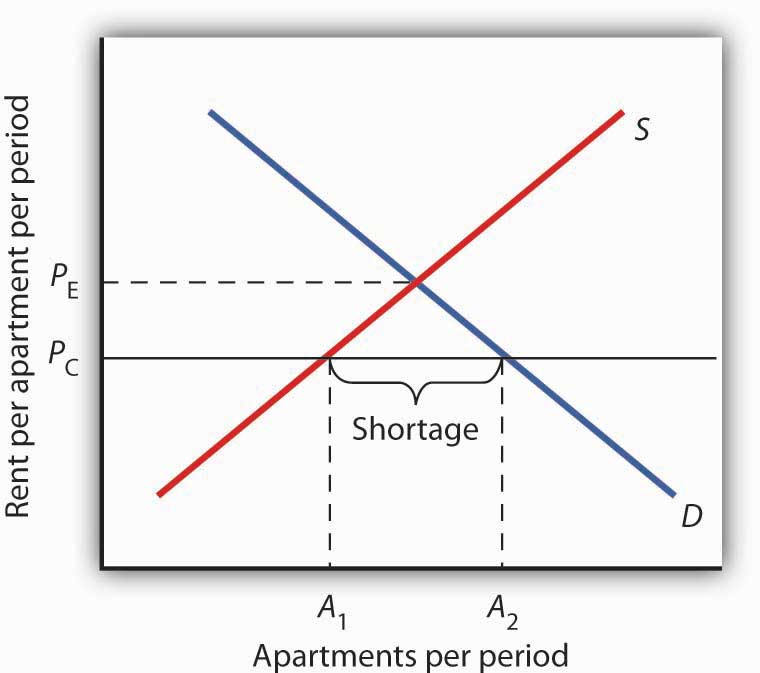
Which leads to a shortage.
This control may be higher or lower than the equilibrium price that the market determines for demand and supply.
Let s consider the house rent market.
These price controls are legal restrictions on how high or how low a market price can go.
Real life example of a price ceiling in the 1970s the u s.
Which leads to a surplus.
Price floors and price ceilings are similar in that both are forms of government pricing control.
Price ceiling is one of the approaches used by the government and the purpose of which is to control the prices and to set a limit for charging high prices for a product.